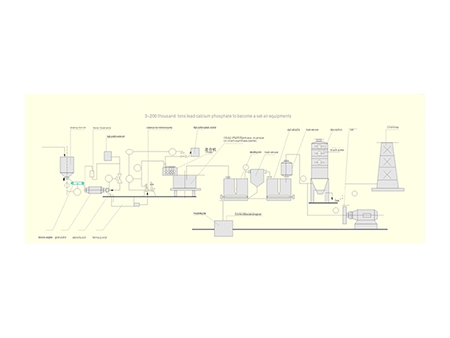
3-300Kt/a SSP/GSSP Fertilizer Plant
Production Flow
While producing the single super phosphate fertilizer, the sulphuric acid and ground phosphate rock have to be mixed together firstly, and then allow the mixture to be cured in the curing room until it is fully cured. During the curing process, the SSP fertilizer manufacturing plant will recycle the waste gas which contains fluorine, and finally, it granulates and dries the material to get the granualated single super phosphate fertilizer. More detailed production process is illustrated in the process flow diagram shown on this page.
During curing process, the mixture should be continuously stirred to increase water evaporation speed and reduce the material temperature, thus ensuring the successful and smooth proceeding of the following production process and improving the material’s physical property. The curing period typically lasts for 3 to 15 days. After curing, the single superphosphate still contains some free phosphoric acid (5.5%-8% P2O5) which brings difficulties in the fertilizer transportation, storage, and application. Therefore, the material has to be neutralized before leaving factory, so as to remove the phosphoric acid.
The GSSP fertilizer production plant supports two kinds of neutralization methods. One is by adding some materials which can act with phosphoric acid rapidly, such as the limestone, bone meal, ground phosphate rock, and more. The other is to remove the phosphoric acid by ammoniation. During ammoniation process, the dosage of ammonia or ammonium salts has to be strictly controlled. After phosphoric acid neutralization, the single superphosphate comes with improved physical property, and offers reduced moisture absorption and agglomeration. After ammoniation, the fertimizer offers increased nitrogen content, which ensures better fertilizing effect.
After neutralization, the single super phosphate fertilizer plant will granulate and dry the single super phosphate to get the granulated fertilizer.
The waste gas containing fluorine is absorbed by the water in the fluorine absorption column or washing tower. Thus, fluosilicic acid is achieved, and it can be further processed into sodium fluosilicate, sodium fluoride, aluminum fluoride, and other secondary products which are regularly applied in chemical, medicine, metallurgy, enamel, building material, and more industries.
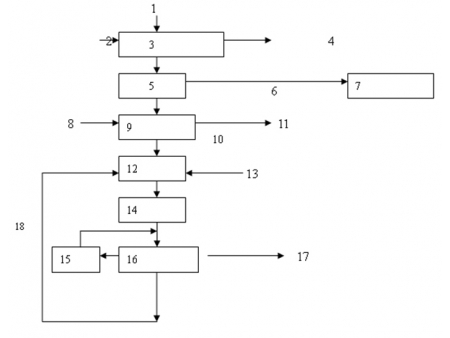
1. Water
2. Ground phosphate rock
3. Mixing
4. Sulfuric acid
5. Curing
6. Gas containing fluorine, water
7. Washing tower
8. Ammonia
9. Neutralization
10. CO
11. Waste gas
12. Granulating
13. Water
14. Drying
15. Crushing
16. Screening
17. Granulated single super phosphate
18. Returned material