Thermocouple Extension & Compensating Wire
Request a Quote
Features
- Material Composition: Made from alloys that match the thermocouple reference wire in the expected temperature range. For example, K-type thermocouples use chromel and alumel alloys, so the extension wire is also made from chromel-alumel alloys.
- Operating Temperature: The rated temperature range of extension wires is lower compared to the thermocouple itself. This allows them to transmit signals from sensors in high-temperature environments to cooler control areas.
- Accuracy: Designed to maintain the original voltage-temperature relationship of the thermocouple. Any deviation can lead to errors, making it crucial to select the correct extension wire type.
- Insulation: Insulated using materials suitable for the environment, such as PVC, Teflon, or fiberglass, to ensure reliable performance.
Differences Between Thermocouple Wire and Extension Wire
| Feature | Thermocouple Wire | Extension Wire |
| Material | Same as Thermocouple Alloy | Matches only within the specified temperature range |
| Temp Change | High (some types up to 1,700°C) | Limited (usually up to 400°C) |
| Cost | Higher | Reduced |
| Purpose | Used for temperature sensing | Extends the temperature signal to instrumentation |
Main Considerations When Choosing Thermocouple Extension Wires
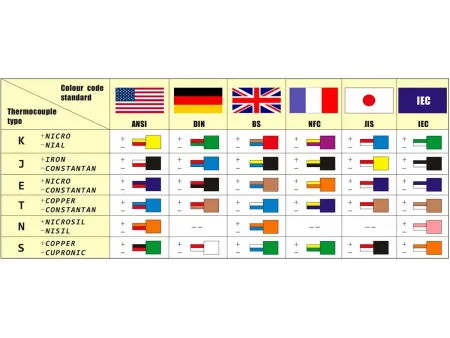
- Match thermocouple type: The extension wire must correspond to the thermocouple type (e.g., K, J, T).
- Operating environment: Ensure that the insulation material is suitable for temperature, humidity, or chemical exposure conditions.
PVC: Flexible, general-purpose.
Fiberglass: High-temperature resistant.
PTFE (Teflon): Chemical and moisture resistant. - Wire gauge: Heavier gauges are needed for long distances or harsh environments to minimize signal loss.
- Shielding: For environments with electrical interference, consider using shielded wire.
- Accuracy: Verify whether the wire meets ASTM or IEC standards for accuracy.
| Thermocouple Type | Compensating Wire Type | Usage | EMF Standard | Precision Grade | General Grade | |||
| Temperature /℃ | Value /μV | Tolerance μV | EMF Range μV | Tolerance μV | EMF Range μV | |||
| K | KX,KCA or KCB | G | -25 | -968 | ±40 | -924~-1012 | ±80 | -880~-1 056 |
| 100 | 4096 | 4052~4140 | 4 008~4 184 | |||||
| H | -25 | -968 | ±40 | -924~-1012 | ±88 | -880~-1 056 | ||
| 100 | 4096 | 4052~4140 | 4 008~4 184 | |||||
| 200 | 8138 | 8094~8182 | 8 050~8 226 | |||||
| J | JX | G | -25 | -1 239 | ±62 | -1177~-1301 | ±123 | -1 116~-1 362 |
| 100 | 5269 | 5207~5331 | 5 146~5 392 | |||||
| H | -25 | -1239 | ±62 | - 177~-1301 | ±123 | -1 116~-1 362 | ||
| 100 | 5269 | 5207~5331 | 5 146~5 392 | |||||
| 200 | 10779 | 10717~10841 | 10 656~10 902 | |||||
| E | EX | G | -25 | -1432 | ±81 | -1351~-1513 | ±138 | -1 294~-1 570 |
| 100 | 6 319 | 6238~ 6400 | 6 181~6 457 | |||||
| H | -25 | -1432 | ±81 | -1351~- 1513 | ±138 | -1 294~-1 570 | ||
| 100 | 6319 | 6238~6400 | 6 181~6 457 | |||||
| 200 | 13421 | 13340~13502 | 13 283~13 559 | |||||
| T | TX | G | -25 | -940 | ±30 | -910~-970 | ±60 | -1850 |
| 100 | 4279 | 4249~4309 | 4189~4339 | |||||
| H | -25 | -940 | ±48 | -892~-988 | ||||
| 100 | 4279 | 4231~4327 | ||||||
| 200 | 9288 | 9240~9336 | ||||||
| N | NX or NC | G | -25 | -646 | ±43 | -603~-689 | ±86 | -560~-732 |
| 100 | 2774 | 2731~2817 | 2 688~2 860 | |||||
| H | -25 | -646 | ±43 | -603~-690 | ±86 | -560~-732 | ||
| 100 | 2774 | 2731~2817 | 2 688~2 860 | |||||
| 200 | 5913 | 5870~5956 | 5 827~5 999 | |||||
| SorR | SC or RC | G | 100 | 646 | ±30 | 616~676 | ±60 | 586~706 |
| H | 100 | 646 | - | - | ±60 | 586~706 | ||
| 200 | 11441 | - | - | 1.381~1 501 | ||||
Applications
- Aerospace: Monitoring engine components
- Power plants: Measuring temperature in boilers or turbines
- Medical equipment: Transmitting signals from sterilization equipment
- HVAC systems: Connecting sensors to control units